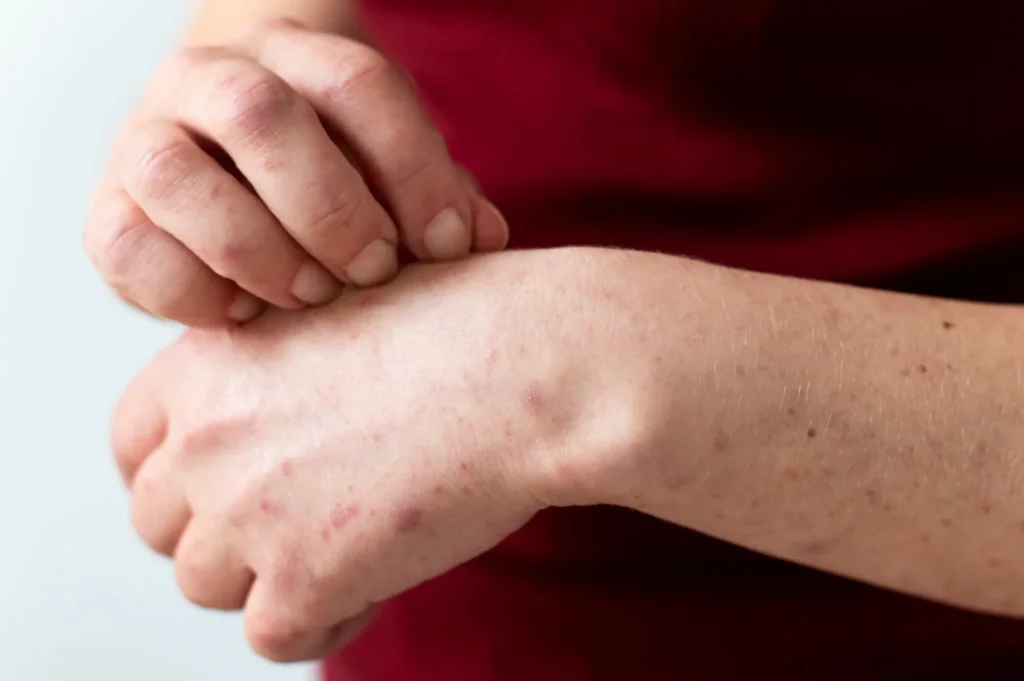
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that occurs when the skin reacts to substances it comes into direct contact with. This reaction can lead to inflammation, redness, itching, and discomfort. While contact dermatitis is not contagious, it can significantly affect daily activities and quality of life if left untreated.
The condition may develop suddenly after exposure or appear gradually with repeated contact over time. Identifying the trigger is an essential part of managing symptoms and preventing future flare-ups.
When the skin is exposed to certain substances, it may become irritated or trigger an immune response. This reaction causes inflammation in the outer layers of the skin, leading to visible changes and uncomfortable sensations.
Symptoms may remain localized to the area of contact or spread beyond the initial exposure site, especially with ongoing irritation or scratching.
Contact dermatitis generally falls into two main categories, each with distinct causes and mechanisms.
Irritant contact dermatitis
This is the most common form and occurs when a substance damages the skin’s protective barrier. It does not involve an immune response and may affect anyone with sufficient exposure.
Common irritants include:
Soaps and detergents
Cleaning products
Acids or solvents
Frequent handwashing or prolonged moisture exposure
Allergic contact dermatitis
This form develops when the immune system reacts to a specific substance after prior sensitization. Even minimal exposure can trigger symptoms once sensitivity has developed.
Common allergens include:
Nickel and other metals
Fragrances and preservatives
Latex
Cosmetics and personal care products
Certain plants, such as poison ivy
Certain individuals may be more likely to develop contact dermatitis due to personal or environmental factors.
Risk factors include:
Occupational exposure to chemicals or irritants
History of eczema or sensitive skin
Frequent exposure to water or harsh substances
Use of fragranced or preservative-heavy products
Repeated contact with known allergens
Understanding personal risk helps guide prevention strategies.
Accurate diagnosis begins with a detailed review of symptoms, lifestyle habits, and potential exposures. Identifying the responsible substance is key to effective treatment.
Evaluation may include:
Physical examination of the skin
Review of skincare, household, and workplace products
Patch testing to identify allergic triggers
Assessment for other skin conditions with similar appearances
A clear diagnosis allows for targeted care and long-term symptom control.
Preventive care plays an important role in minimizing flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin.
Helpful strategies include:
Using fragrance-free and gentle skincare products
Wearing protective gloves or clothing when needed
Moisturizing regularly to support the skin barrier
Avoiding known allergens and irritants
Following personalized skin care recommendations
Ongoing care helps prevent recurrence and supports skin healing.
Contact dermatitis can be frustrating, but with proper diagnosis and individualized treatment, symptoms can be effectively controlled. Identifying triggers and maintaining consistent skin care habits are key to long-term relief.
If ongoing skin irritation or rashes are affecting your comfort or confidence, schedule an appointment to receive expert guidance and personalized care.

Flat fee for tele visits with included services: $100
(571) 399-5132
Fax
(703) 723-9800
Location
19455 Deerfield Avenue, Suite 207, Leesburg, VA 20176
Monday and Thursday
9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Tuesday, Wednesday
9:30 AM - 3:30 PM
Every other Friday
Upon Request
Monday and Thursday
9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Tuesday, Wednesday
9:30 AM - 3:30 PM
Every other Friday
Upon Request
Directly across from Inova Loudoun Hospital, first building on Deerfield Drive on the left, with easy access from Route 7.
Copyright 2026 Allergy Asthma Immunology. All Rights Reserved.