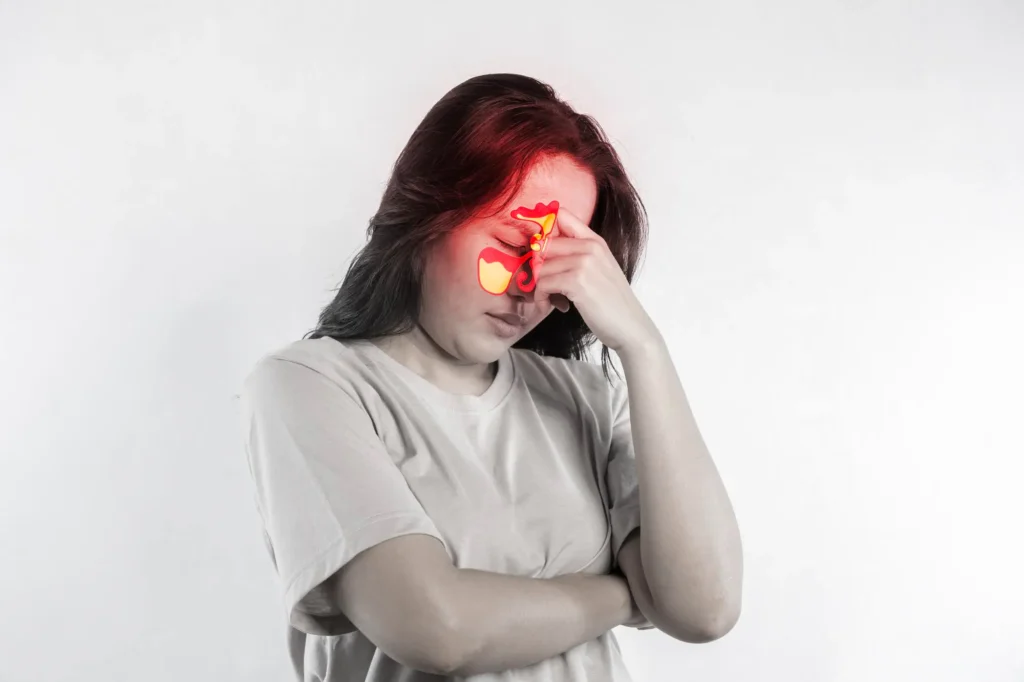
Sinus headaches are caused by inflammation and pressure within the sinus cavities, leading to pain and discomfort in the face and head. They commonly occur alongside sinus infections, allergies, or chronic nasal inflammation. The pain may feel deep, persistent, and concentrated around the forehead, eyes, or cheeks.
Although sinus headaches are frequently assumed to be the cause of facial pain, proper evaluation is important, as other headache types can produce similar symptoms.
Sinus-related headaches typically cause a dull, aching pressure rather than sharp or throbbing pain. Discomfort often worsens with changes in head position or during periods of congestion.
Common features include:
Pressure around the forehead, eyes, or cheeks
Pain behind or between the eyes
Facial tenderness to touch
Worsening pain when bending forward
Increased discomfort in the morning
Sensation of fullness in the face
Pain may occur on one or both sides of the face, depending on sinus involvement.
Sinus headaches usually develop when sinus drainage pathways become blocked, allowing mucus to build up and create pressure.
Common contributing conditions include:
Acute or chronic sinus infections
Allergic rhinitis (seasonal or perennial allergies)
Nasal polyps
Deviated nasal septum
Upper respiratory infections
Ongoing nasal inflammation
Persistent sinus congestion increases the likelihood of recurrent headaches.
Sinus headaches often occur with other nasal and sinus-related symptoms, helping distinguish them from migraine or tension headaches.
Associated symptoms may include:
Nasal congestion or blockage
Thick nasal discharge
Postnasal drip
Reduced sense of smell
Ear pressure or fullness
Fatigue
Low-grade fever during infections
The combination of facial pain and nasal symptoms often points toward a sinus-related cause.
Accurate diagnosis begins with a thorough review of symptoms and medical history. Because migraines are commonly mistaken for sinus headaches, careful evaluation is essential.
Diagnostic assessment may include:
Physical examination of the nose and sinuses
Nasal endoscopy to visualize sinus drainage pathways
Imaging studies, such as CT scans, for chronic or severe symptoms
Allergy testing to identify underlying triggers
Identifying the true source of head pain allows for more effective treatment.
Preventive care can help reduce the frequency and severity of sinus headaches, especially for individuals with allergies or chronic sinus conditions.
Helpful strategies include:
Managing seasonal or environmental allergies
Using daily nasal sprays as prescribed
Avoiding known triggers and irritants
Staying well-hydrated
Treating nasal congestion early
Consistent sinus care plays an important role in long-term relief.
Sinus headaches can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but effective treatment is available once the underlying cause is identified. With proper evaluation and individualized care, many patients experience lasting relief and fewer recurrences.
If facial pressure or head pain is affecting your comfort or productivity, schedule an appointment to explore treatment options and restore sinus health.

Flat fee for tele visits with included services: $100
(571) 399-5132
Fax
(703) 723-9800
Location
19455 Deerfield Avenue, Suite 207, Leesburg, VA 20176
Monday and Thursday
9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Tuesday, Wednesday
9:30 AM - 3:30 PM
Every other Friday
Upon Request
Monday and Thursday
9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Tuesday, Wednesday
9:30 AM - 3:30 PM
Every other Friday
Upon Request
Directly across from Inova Loudoun Hospital, first building on Deerfield Drive on the left, with easy access from Route 7.
Copyright 2026 Allergy Asthma Immunology. All Rights Reserved.